The 4 Pillars of Successful Customer Enablement Strategy
The Gap in Customer Enablement Strategies
Customer Enablement is a misunderstood discipline that stems from industry practitioners applying a narrow scope for customer enablement. This parochial thinking creates a gap in customer enablement practices within an organization.
Multiple teams within a business play a role in customer enablement. There are customer training teams who are enabling their customers through training. Product managers employ product insights and in-product walkthrough flows and this is considered to be customer enablement. Customer support roles and customer success members are also in the business of enablement. The organizational gap isn’t at the tactical level, it exists at a strategic level. These different siloed functions are all engaged in customer enablement and employ their processes, systems, and tools to enable their customers in their own way. When companies are only focused at the tactical level team approaches end up quite disadvantageous.
A strategic approach to customer enablement demands that the organization inspect these efforts through the lens of its customers. When they do so, the picture becomes clearer. Understanding the key concepts of customer enablement and the 4 components that make it possible are the first steps to taking a holistic approach to customer enablement.
The 4 Pillars of Customer Enablement
Customer Enablement is a strategic initiative that spans multiple internal teams with a singular focus on helping customers successfully navigate their customer journey. To drive success in customer enablement, organizations have to consider four primary pillars that make up customer enablement.
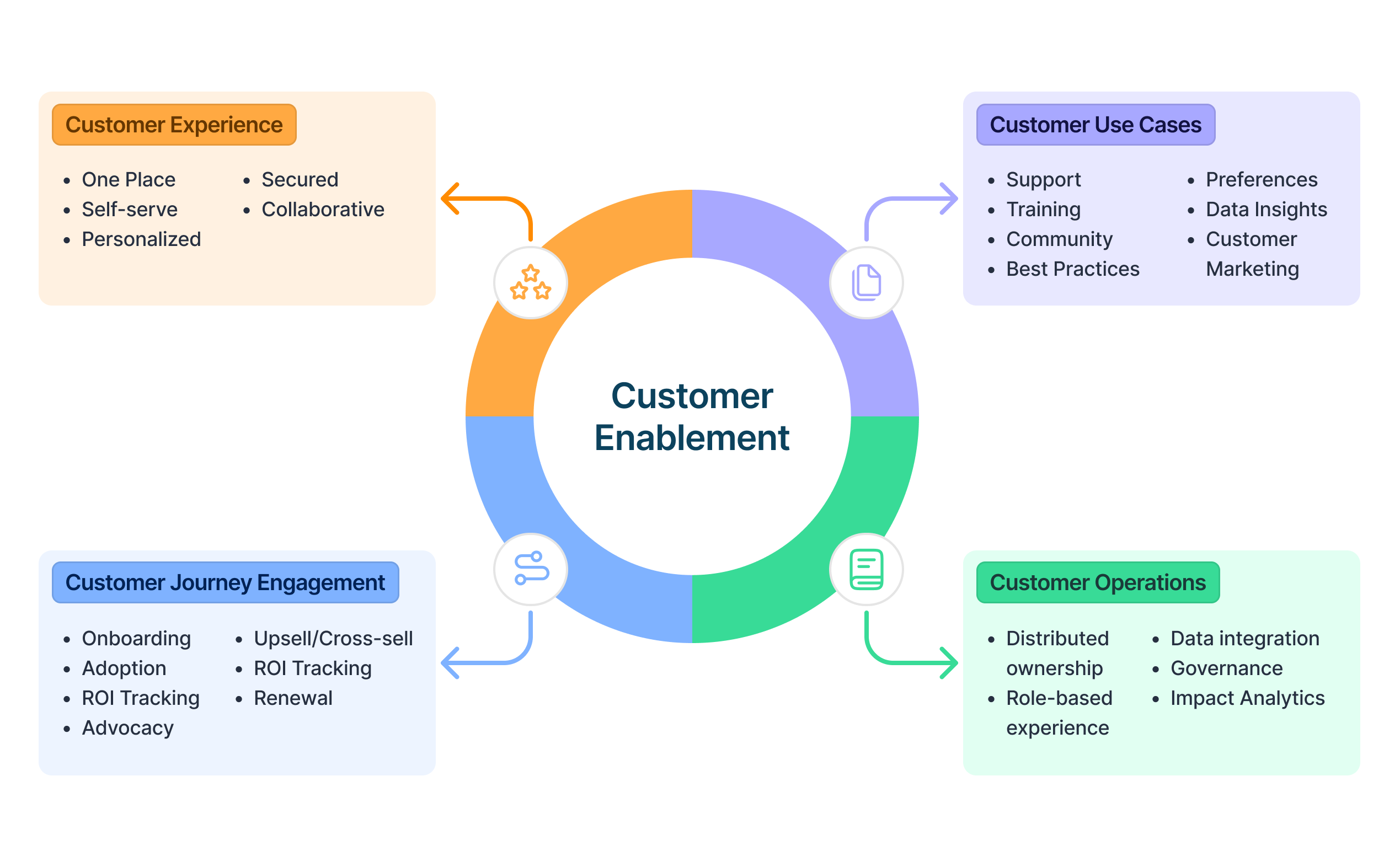
1. Customer Experience:
Customer Experience is a vital component of an organization’s customer enablement strategy. Without a seamless, secure, and targeted experience, customer engagement dips. The lack of customer engagement defeats the purpose of the entire enablement program. Therefore, organizations need to strive to deliver an experience that includes the following.
Requirements for an enabled customer experience
Deliver one place for the customer to go: Customers should not be required to access multiple apps and portals. Organizations should work towards a single digital experience.
Create a self-serve environment: Most organization’s customer interactions are reactive. Customer-facing teams are responding to a customer’s query or need. This not only introduces friction for the customers, it also increases your enablement costs. Organizations should aim to enable their customers on their customer’s time by activating self-serve experiences.
Provide a personalized experience: Organizations are increasingly serving a varied set of customers. This variability can result in an overwhelming experience for their customers. Therefore serving relevant information and use cases to the customers should be a priority.
Must be seamless and secured: To deliver a seamless customer experience, organizations should be able to arm customers with publicly available and confidential information. A secure experience is vital to build trust and credibility.
Offer two-way collaboration: Serving a one-sided communication platform is not enough. Customers should be equipped with tools and capabilities to provide feedback and communicate back with the stakeholders.
2. Customer Use Cases
Strategic customer enablement programs integrate multiple touchpoints—onboarding, training, community engagement, support resources, and knowledge management—all aligned with the customer journey and core business objectives. As we've established, delivering these diverse enablement functions through a unified digital experience is essential for program success, creating a seamless pathway that supports customers at every stage of their relationship with your organization.
An organization will likely use different vendors to support these use cases. It is important to explore integration options to deliver a seamless customer experience. Important concepts like security, personalization, content discovery, etc are vital when considering integration options.
Furthermore, as organizations consider investing in new use cases, they should explore if the enablement platform can support those use cases natively versus investing in a specialized point solution and dealing with integration hassles.
3. Customer-Journey Engagement
Organizations should approach enablement through the lens of their customer’s journey. Rather than applying one-size-fits-all enablement tactics, organizations should develop stage-specific enablement strategies that address the unique challenges customers face as they progress from newcomers to mature users. This journey-aligned approach transforms generic customer interactions into precision enablement, targeting the exact needs of customers based on where they stand in their relationship with your product or service. Approaching enablement from a customer journey context helps in multiple ways:
Personalization: Personalizing the experience based on the customer’s journey is a big enablement win. A customer who is in the onboarding phase of their journey has very different needs from that of an established customer.
Automation: As the customer moves through their journey, there are opportunities to automate enablement paths. For instance, when a customer completes the onboarding phase, they should be enrolled in customer training to drive adoption.
Tactical Campaigns: Once a customer enablement foundation is in place, organizations can drive tactical campaigns to address gaps in the customer’s journey. If onboarding is a challenge, then stakeholders can invest in the onboarding stage by running tactical campaigns. Tracking customer journey stages provides an actionable framework to deliver enablement ROI.
Customer Owners: It is not uncommon to have different stakeholders within the organization for different journey stages. Customer success owning the onboarding phase, support owning the maturity stage, and account management owning the renewal stage are not uncommon.
4. Enablement Operations
Customer Enablement requires a systematic operational approach to ensure consistency and effectiveness across the entire customer journey. Unlike point solutions that operate in isolation, comprehensive enablement spans multiple teams and touchpoints, necessitating a central coordinating function: Enablement Operations.
Enablement Ops serves as the crucial connective tissue between departments, establishing governance structures that maintain quality and consistency while allowing specialized teams to contribute their expertise. This function owns the enablement technology stack, ensuring that tools and platforms work together to deliver a seamless customer experience rather than creating additional silos.
Key responsibilities of Enablement Operations include:
Defining and maintaining enablement standards and best practices
Managing the enablement technology infrastructure
Coordinating content creation and maintenance across teams
Measuring enablement effectiveness and driving continuous improvement
Facilitating cross-functional collaboration and alignment
Ensuring security and compliance across all enablement activities
Without a dedicated Enablement Ops function, organizations risk creating disconnected experiences as different teams pursue their enablement initiatives without coordination. This centralized approach doesn't replace specialized expertise in areas like training, support, or product education—rather, it harmonizes these efforts to create a coherent, efficient enablement engine that drives measurable business outcomes.
Customer Enablement Pillars Drive Holistic Success Strategy
Every enablement use case is vital. But when organizations invest in solving these siloed use cases independently without any cohesive customer enablement strategy, they are bound to deliver a poorer customer experience. These myopic steps will not only impact customer satisfaction, but they will also impact the effectiveness of the individual use cases.
Organizations that take a holistic approach to Customer Enablement stand a greater chance to deliver winning customer experiences, drive enablement costs with the help of a central framework, and drive revenue growth.