Dominate any industry with a Market Penetration Strategy

Table of Contents
What is Market Penetration?
Market Penetration shows how many customers use a company’s product over its competitor. Many companies use this strategy to adjust their marketing strategy to make it more optimal for sales.
Companies also use market penetration to understand their market size to adjust their marketing strategy accordingly.
For example, if Apple (electronic company) sells its products to a country that houses one hundred million people but only fifty million own Apple products, then fifty million people are yet to experience these products.
With this information, you can adjust all strategies accordingly to ensure the company reaches the remaining fifty million.
[elementor-template id="5662843"]
How Market Penetration Started?
This strategy stems from the original Ansoff Matrix developed by H. Igor Ansoff from the Harvard Business Review.
Ansoff wrote the article “Strategies for Diversification,” which shows the four strategies to increase sales. This matrix primarily focused on understanding sales volume with the total target market for the product.
What is Market Penetration Strategy?
This strategy entails generating maximum sales for a product in a competitive market. The concept of penetration is entering into a market and eventually domineering over the other competitors.
Market Penetration strategy helps companies expand their reach to as much of the target market as possible.
Companies look for a good market penetration rate to determine the Total addressable Market (TAM). Companies use the TAM when solving their Market Penetration Rate.
Value of Market Penetration Strategy
Market Penetration strategy primarily helps companies determine their product’s impact, especially in a highly competitive market.
A smaller company or startup can use a Market Penetration strategy to determine the customers they need to compete with other established companies. This strategy comprises many companies’ marketing strategies to help them adjust their strategy accordingly.
How to Measure Market Penetration
Here are a few steps to start measuring a company’s market penetration for their products. Despite its simplicity, more effort must go into analyzing these statistics to make the best decision for their marketing strategies.
Identify Potential Customers to Target
The company must first identify the potential customers their product will impact. Determine first their demographic data to help with making the target market as accurate as possible.
Consider becoming more precise with the demographic data to make your target more vivid and tangible.
You can consider these factors to help you dial into the target customer:
- Age
- Gender
- Income bracket
- Marriage status
- Employment status
- Nationality
These factors help establish the target profile for the product’s potential consumers. Concretizing these factors also prevent excess effort for consumers not interested in the product.
Prevent generalizing too much with the target consumers; as it provides a false impression of the penetration rate, making it more difficult to develop a functional marketing strategy.
Take note that a product’s market size is significantly different from other products in the same company.
For example, if company A is in the fashion industry, the pants section will have a completely different market size than the t-shirt section.
Calculate the Total Size of Your Market
After determining the product's consumers' demographic profiles, determine the target market's total size.
The number of consumers is a most reasonable estimation of the actual number of consumers. However, prevent over-generalizing or overestimating the number of consumers.
This size significantly affects the normal market penetration calculation done after generating the value. Other companies also multiply the company’s average annual revenue from these customers in the market to achieve a more concrete market size.
Many companies also calculate each product’s market size rather than generalizing everything.
This strategy allows the company to adjust its marketing strategy according to the consumers’ needs.
Determine the Normal Market Penetration for Your Product
The product’s normal market penetration is usually a percentage range determined by the company.
The company usually estimates the percentage from careful and calculated data from past experiences. Startups, however, use data from other companies to calculate the average percentage range for their product.
For example, suppose Company A estimates a normal market penetration between three and five percent (3% - 5%) for their 100,000 consumers.
They will multiply the number of consumers by the ranges stated to get the normal market penetration.
Example:
100,000 * .03 = 3,000
100,000 * .05 = 5,000
Normal Market Penetration = 3,000 - 5,000 customers
Remember to always make the rates as realistic as possible. Refrain from over and under compensating to create a more normal market penetration.
More realistic calculations allow more practical marketing adjustments for the company’s marketing strategies.
Compare the Estimated Market Penetration Range Between Your Customers
After determining the company’s Normal Marketing Penetration rate, start comparing it between the number of customers you need to earn a profit.
Sometimes, a company’s normal penetration range is not sufficient to breakeven.
Using the same example above, if the company needs fifteen thousand (15,000) customers to breakeven and its normal penetration range is 3,000 to 5,000 customers, the company needs to adjust its penetration range or product price.
Adjusting a company’s penetration range might increase the discrepancy, especially if the range is relatively more accurate than the adjusted one.
Some companies result to lowering their production price to lessen the number of customers to breakeven.
Manufacturing companies can use this accounting format to calculate the cost of their products [cost of good sold]:
Direct Materials xx
Indirect Labor xx
Manufacturing Overhead xx
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Cost of Manufacturing xx
Work-in-process, beginning xx
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cost of Work Put Into Process xx
Less: Work-in-Process, ending (xx)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cost of Manufactured Goods xx
Finished Goods, Beginning xx
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total Goods Available for Sale xx
Less: Finished Goods Ending (xx)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cost of Sales xx
After calculating the company’s cost of sales, the company can now price its products accordingly.
If the target customers are relatively lower than the number of customers needed to breakeven, consider lowering the product’s cost of sales than altering an accurate Normal Market Penetration.
Advantages of High Market Penetration
Higher market penetration means that more customers are inclined to purchase the company’s product.
Companies can make more general strategies to reach these customers since the market penetration is higher. However, the company may also be subject to more competitors for products with higher market penetration.
A higher market penetration also means a relatively more impactful product. A product can only sell if many customers find this product helpful in their daily activities.
Conversely, lower market penetration can mean that the product might be too expensive for more people to purchase. Large market penetration means the product is relatively more accessible to more consumers. It also means their sales communication has been very effective.
How to Calculate Market Penetration
To calculate the market penetration, use the product sales volume and divide among the other competitors' products. After, multiply the answer by 100 to get the market penetration rate.
A higher sales volume usually means a higher appreciation for the product. An acceptable penetration rate primarily depends on the number of competitors in the industry.
However, a good penetration rate if it is significantly higher than the other competitors in the industry.
The Ansoff Matrix
Another term for the Ansoff Matrix is the Product/Market Expansion Grid. H. Igor Ansoff first devised the Ansoff Matrix in his publication in the Harvard Business Review in 1957.
Ansoff wrote the original article, "Strategies for Diversification," where he proposed a concrete strategy for marketers and businessmen to strategically scale their business.
This matrix is a tool that companies use to plan and strategize for their future growth. The matrix incorporates four strategies to allow a more concrete action plan for a product’s growth.
The Four Basic Growth Strategies of the Ansoff Matrix
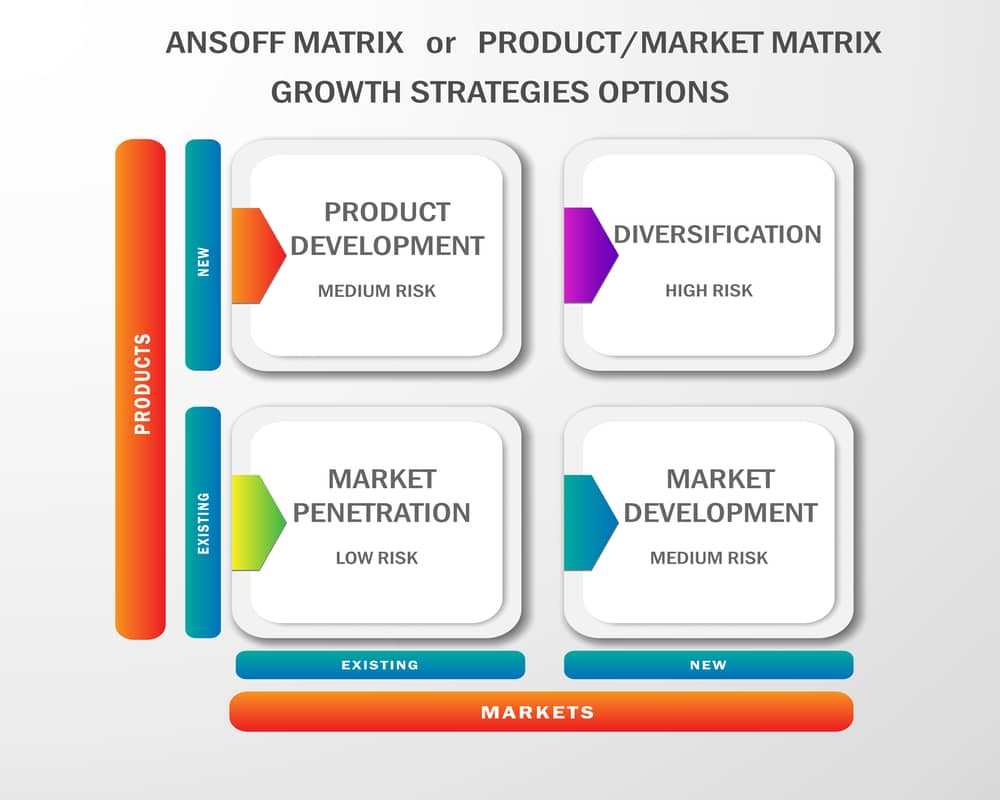
The four basic growth strategies proposed by Ansoff are
- Market Penetration
- Market Development
- Product Development
- Diversification
Let's discuss extensively these strategies and provide concrete applications for each.
Market Penetration: Existing Products in Existing Market
The market penetration strategy allows companies to scale their business by increasing the product’s market shares.
Companies use this strategy to gain more exposure by acquiring income from different marketing participants. Other companies also use market penetration strategy to adjust their prices strategically to take out other competitors in the same market.
Market Penetration creates numerous marketing strategies. However, more practical results can stem from making prices more appealing to target customers.
Suppose the company is relatively more accomplished and with a reasonable price margin without generating a net loss. In that case, the company can lower its prices to make it more appealing than its competitors.
Customers will be inclined to own more affordable products than others.
Many companies may also run different promotions to increase the product’s publicity.
Established companies may also buy smaller companies to acquire the rights to sell profitable products in the same marketplace.
Product Development: New Products in Existing Market
Product development refers to improving an existing product to make it more appealing and acceptable in a highly competitive market. A highly competitive market encourages more innovative ideas for customers to enjoy.
A company must incorporate an innovative mindset to compete against its other more mature competitors.
Usually, companies invest significant amounts to fund research and development for a product.
The company can patent this innovation to secure its innovation for a set number of years.
Others might consider purchasing a competitor’s product and improve it to make it more appealing for customers.
Established companies choose to partner with similar companies to collaborate on a product their consumers could appreciate.
One of the greatest examples of this kind of strategy is the Pharmaceutical industry. Pharmaceutical companies continue to outwork each other by dedicating time, research, and development to produce products significantly superior over the others.
Car companies create different features to stand out from their other competitors. Car companies also choose to partner with other companies to collaborate on a car with the two companies' characteristics.
Suzuki and Toyota have a global partnership, Toyota acquired 4.94% ownership of Suzuki through shares. Both of these companies have agreed to share specific technology and cars in various markets. These kinds of agreements also helps them with their market penetration strategy.
Example: Suzuki Brezza and Toyota Urban Cruiser is the same car, they just change the logos to differentiate the brand and sell it.
Market Development: Existing Products in New Markets
This strategy allows companies to expand to markets other than their original market. Expanding markets could mean expanding their products to different countries or engage more demographic profiles to their products.
Companies also choose to expand regionally to different states that do not have a highly competitive market in that industry.
Incorporating this strategy might result in more money for this expansion, especially if it is for different countries. Expanding to different countries may also increase tax rates and barriers the company needs to shoulder.
One of the greatest examples of market development is Apple’s ability to expand internationally.
The company invests much money in expanding its products worldwide to beat competitive markets in all countries.
Diversification: New Products in New Markets
Diversification is a strategy that involves entering a different market with another product. This strategy is considered one of the riskiest endeavors companies consider.
Some companies have less experience in the market than the other mature companies in the industry. Companies might also need to invest more in hiring professionals for a different industry.
A company may consider two types of diversification.
Related diversification
Related diversification refers to entering a similar market to the original market. For example, a cell phone company may choose to enter into electronic accessories like headphones, chargers, etc.
Electronic companies may also explore other electronics aside from cellphone like tablets and computers.
Unrelated diversification
unrelated diversification refers to entering a completely unrelated market than the original. The bench, for example, entered the food industry while their primary business is clothing apparel.
How to do Strategic Planning with the Ansoff Matrix
SWOT Analysis and the Ansoff Matrix
SWOT refers to the four company aspects, namely:
- Strengths
- Weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Threats
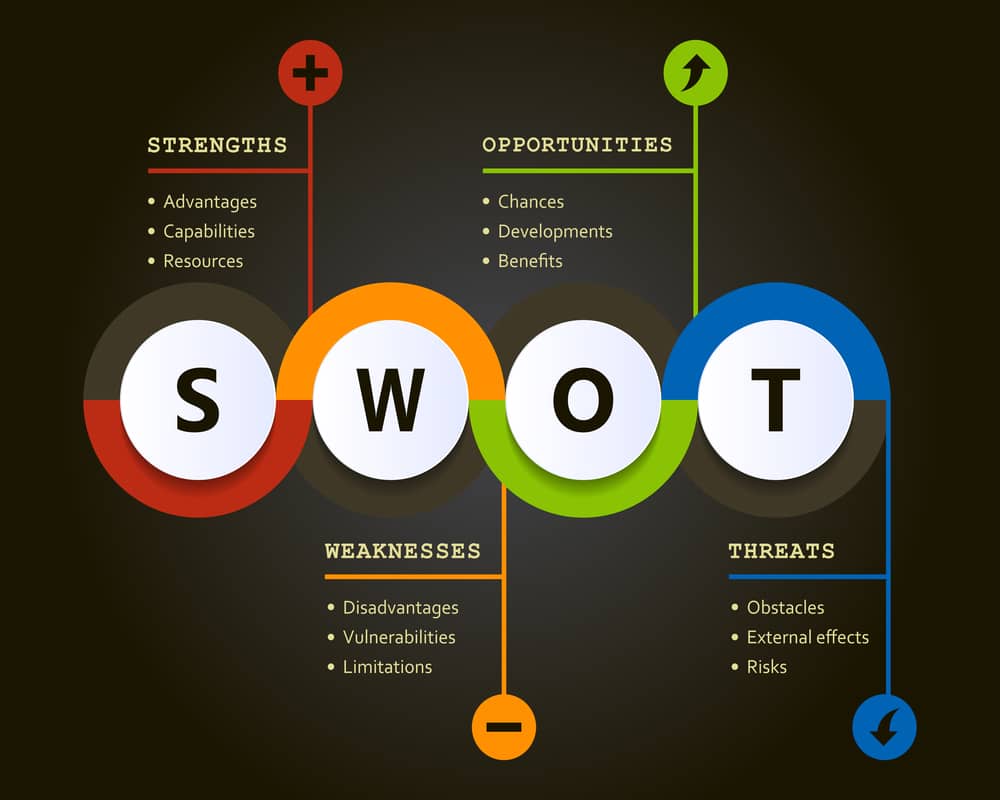
Companies use this analysis in creating their business plan to ensure that their plans cater to their strengths and avoid their weaknesses.
Many companies incorporate the Ansoff Matrix when determining company threats. These threats are significant factors that can hinder a company’s growth.
For example, understanding the strategy to incorporate from the Ansoff Matrix can help determine the strategic decision threats.
For example, a diversification strategy can involve a significant loss when entering a completely different market the company is inexperienced in.
PESTLE Analysis and Ansoff Matrix
Another tool companies incorporate in their business strategy is the PESTLE Analysis. PESTLE refers to the six different factors affecting a company’s growth, namely:
- Political
- Environmental
- Social
- Technological
- Legal
- Economical
The Ansoff matrix helps analyze these factors, especially when incorporating the strategy into a marketing plan. After deciding the strategy to incorporate, the company may use the PESTLE analysis to determine the most important factors for the company’s growth.
What is Market Penetration and Market Development?
Market Development
Market development refers to placing an existing product in different markets. As stated, market development refers to expanding a company’s target market to different demographic profiles.
The example given was Apple's ability to expand its market to different countries and states to increase its exposure and sales volume.
This strategy allows the company the opportunity to expand their market to unavailable customers before. This strategy allows more people to appreciate the product which was unavailable to them.
Strategies of Market Development
Expanding Product to New Users
Companies may consider expanding their product to users unfamiliar with the product. The company must decipher a way to entice non-users to use the product.
Companies resolve this dilemma by including new product features to allow non-users to try them out. Others provide promos and discounts that are appealing enough to non-users.
Many companies also choose to incorporate different advertising strategies to prove to their consumers why they should buy the product and some build a trustable brand with content marketing.
Convincing Consumers from Other Competitors
Companies would try to outperform other competitors to attract their competitors’ loyal customers.
Companies would improve their product significantly than their competitors for the other consumers to purchase their products. Some companies create advertisements portraying a comparison between their product and an inferior competitor.
Customers are more inclined to buy from a company that proves a significant difference from the others.
Some companies would request their regular customers provide testimonials to convince other consumers to buy their product. Other companies lower their prices significantly to compete against the other high prices in the industry.
Prove Distinction from Other Companies
The best way to achieve a good favorability over other competitors is to prove your product is different from the others.
Some companies change the packaging while others completely change their product. If the product is completely the same, the consumer is more inclined to choose either company, making it more difficult to find loyal customers.
However, if the company proves its distinction, the customer will shift over to the superior company instead.
Market Penetration and Market Development Explained
Market Penetration and Market Development usually go together in creating a very good marketing strategy.
A company must first determine a product’s market penetration before developing a market development strategy.
Understanding its correlation is the best way to apply all these concepts to a company’s growth.
For example, Company A must first find its market penetration rate to determine if the market is suitable for them.
If their penetration range is relatively smaller than the customers they need to breakeven, they may consider expanding their target market to different industries (market development).
If the company refuses to follow the process, the company might enter a different industry without knowing that the original market was completely suitable for its growth.
In other words, the company could have incorporated a more affordable, efficient, and effective strategy rather than expanding to a different market.
Overall, the company must first determine the market penetration rate before developing a strategy for its products.
Examples of Market Penetration
Apple
One of Apple’s greatest strategies is dominating the electronics industry through the products they develop.
Apple has a market penetration rate of 19.2%, while Samsung has a market penetration rate of 18.4%. Apple constantly releases products in magnitude to gain the largest market share over its competitors.
The company uses this market share to expand exponentially to different companies to increase revenue for more innovations and development.
Apple uses numerous calculations to develop the strongest strategy to gain maximum revenue for its product.
Nike
Nike uses its popularity to take most of the market shares by selling its shoes to as many people as possible.
Nike uses its popularity to encourage other people to purchase their clothing apparel. This company also incorporates different athletes to encourage their fans to buy their shoes.
Nike's primary goal is to expand its reach by selling its products to all the industry's sports fans. Its numerous endorsements from different players provide consumers the assurance of the quality their sports apparel provides.
Key Takeaways
We extensively discussed everything about the market penetration strategy. We incorporated market penetration into the Ansoff matrix to understand its relation to the different strategies a company can use.
The market penetration strategy is one of the best ways to understand how a product sits in a highly competitive market.
Companies use this knowledge to carefully adjust their marketing strategy to generate the optimal revenue possible through their unique market penetration strategy.